“As we continue to see the global macroeconomic environment improve, we expect U.S. industrial manufacturing executives, bolstered by strong balance sheets, to more aggressively compete for businesses in international markets and increase capital expenditures,” said Bobby Bono, U.S. industrial manufacturing leader, PwC.
Here are some survey findings:
- 85 percent of survey respondents expect positive revenue growth for their own companies in 2014, with 13 percent forecasting double-digit gains, and only 3 percent expecting negative growth.
- 60 percent of the Q4 2013 respondents plan new net hiring in 2014, but will do so at a more moderate pace. Only 3 percent plan to reduce the number of full-time equivalent employees, and 37 percent will neither add nor decrease employment. The most sought-after employees will be skilled labor (42 percent), followed by professionals/technicians (30 percent) and production workers (28 percent).
- 29 percent of respondents report increased international sales, up from 18 percent the prior quarter.
“As the shale energy revolution continues to ramp up in the U.S., we are seeing significant moderation in concerns regarding energy costs among industrial manufacturers, reflecting the positive influence that shale gas is having from investment, operational, and demand standpoints. The low-cost energy also provides a significant incentive for manufacturers to shorten their supply chain and bring production facilities back to the U.S.,” Bono added.
A survey conducted by the Boston Consulting Group confirms the impact of the shale boom on manufacturers’ re-shoring operations, as reported in The Financial Times.
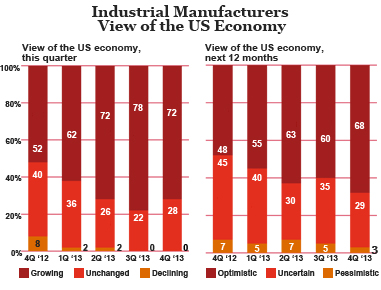
Additionally, the Q4 2013 PwC Manufacturing Barometer indicates that Cybersecurity continues to be a major area of focus for industrial manufacturers:
75 percent claim to have a methodology to detect the effectiveness of their organization’s security programs, and 82 percent cite having a formalized plan in place for reporting and responding to cybersecurity events. Over the past 12 months, only a limited number (15 percent) report an increase in cybersecurity events. When polled, U.S. industrial manufacturers cite hackers as the greatest cybersecurity threat to their business (69 percent), followed by current/former employees (26 percent) and activists/activist organizations (7 percent).
Of survey respondents, 38 percent indicate that their business made use of important IT innovations in the past 12 months. The two business sectors leading the way for important IT innovations are manufacturing processes (52 percent) and security/cyber threats (43 percent).
“U.S. industrial manufacturers are embracing IT innovations to both mitigate risks and improve their long-term prospects. In addition to IT investments to combat cyber and information threats, we are seeing manufacturers adapt new technologies and innovations including cloud and mobile computing, and big data and analytics. These important IT investments are helping forward-looking businesses guard against disruptive technologies that are changing the manufacturing landscape, while providing them with an opportunity to adjust their business models, improve their processes, and find new opportunities to grow,” Bono stated.
Additionally, the National Association of Manufacturers commends the partnership between the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and the private sector to improve cybersecurity. “Cybersecurity is tantamount to economic and national security. Defending against cyber threats is a top priority for manufacturers,” said NAM Vice President of Tax, Technology and Domestic Economic Policy Dorothy Coleman before the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation at a July 2013 meeting.